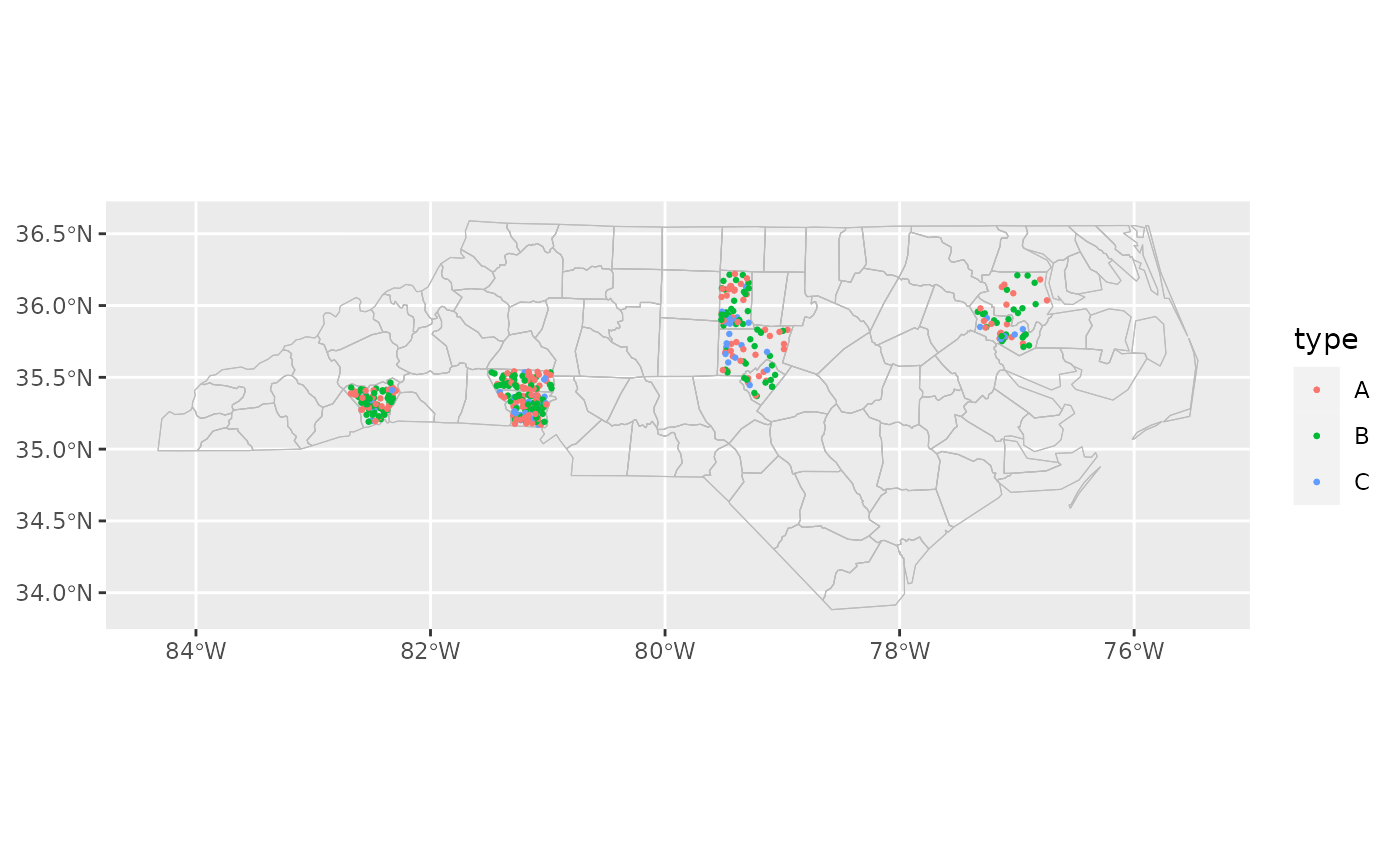
Each row of data is drawn as a single point inside the geographic area. This has similar strengths to a standard scatter plot, but has the potential to be misleading by implying that there is significance to the exact placement of the points.
Usage
geom_geoscatter(
mapping = ggplot2::aes(),
data = NULL,
stat = "geoscatter",
position = "identity",
...,
feature_type = NA,
sample_type = "random",
inset = NA,
map_base = "clip",
map_inset = "auto",
na.rm = TRUE,
show.legend = "point",
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
stat_geoscatter(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = "sf_inset",
position = "identity",
...,
feature_type = NA,
sample_type = "random",
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping, data, stat, geom, position, na.rm, show.legend, inherit.aes, ...
See
ggplot2::geom_sf().- feature_type
Type of map feature. See
feature_types()for a list of registered types. IfNA, the type is guessed based on the values infeature_names.- sample_type
sampling type (see the
typeargument ofsf::st_sample())."random"will place points randomly inside the boundaries, whereas"regular"and"hexagonal"will evenly space points, leaving a small margin close to the boundaries.- inset
Inset configuration; see
configure_inset(). IfNA(the default), this is inherited from the coord (seecoord_sf_inset()).- map_base
Controls the layer with the base map. Possible values are
"normal"to create a layer as though the inset were not specified,"clip"to create a layer with the inset viewport cut out, and"none"to prevent the insertion of a layer for the base map.- map_inset
Controls the layer with the inset map. Possible values are
"auto"to choose the behaviour based on whetherinsetis specified,"normal"to create a layer with the viewport cut out and transformed, and"none"to prevent the insertion of a layer for the viewport map.
Aesthetics
The location aesthetic is required.
geom_geoscatter() understands the same aesthetics as ggplot2::geom_point().
Examples
library(ggplot2)
cartographer::nc_type_example_2 |>
ggplot(aes(location = county)) +
geom_boundaries(feature_type = "sf.nc") +
geom_geoscatter(aes(colour = type), size = 0.5) +
coord_automap(feature_type = "sf.nc")