Use 'cartographer' to attach a spatial column to the data based
on place names in another column. The spatial data is then reduced to
coordinates in the same way as stat_sf_coordinates().
Usage
stat_automap_coords(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = "sf_inset",
position = "identity",
...,
feature_type = NA,
na.rm = TRUE,
inset = NA,
fun.geometry = NULL,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping, data, geom, position, na.rm, show.legend, inherit.aes, fun.geometry, ...
- feature_type
Type of map feature. See
feature_types()for a list of registered types. IfNA, the type is guessed based on the values infeature_names.- inset
Inset configuration; see
configure_inset(). IfNA(the default), this is inherited from the coord (seecoord_sf_inset()).
Computed variables
- geometry
sfgeometry column representing the points- x
X dimension of the simple feature
- y
Y dimension of the simple feature
- x_inset
X dimension of the simple feature after inset transformation
- y_inset
Y dimension of the simple feature after inset transformation
- inside_inset
logical indicating points inside the inset viewport
- inset_scale
1 for points outside the inset, otherwise the configured inset scale parameter
Examples
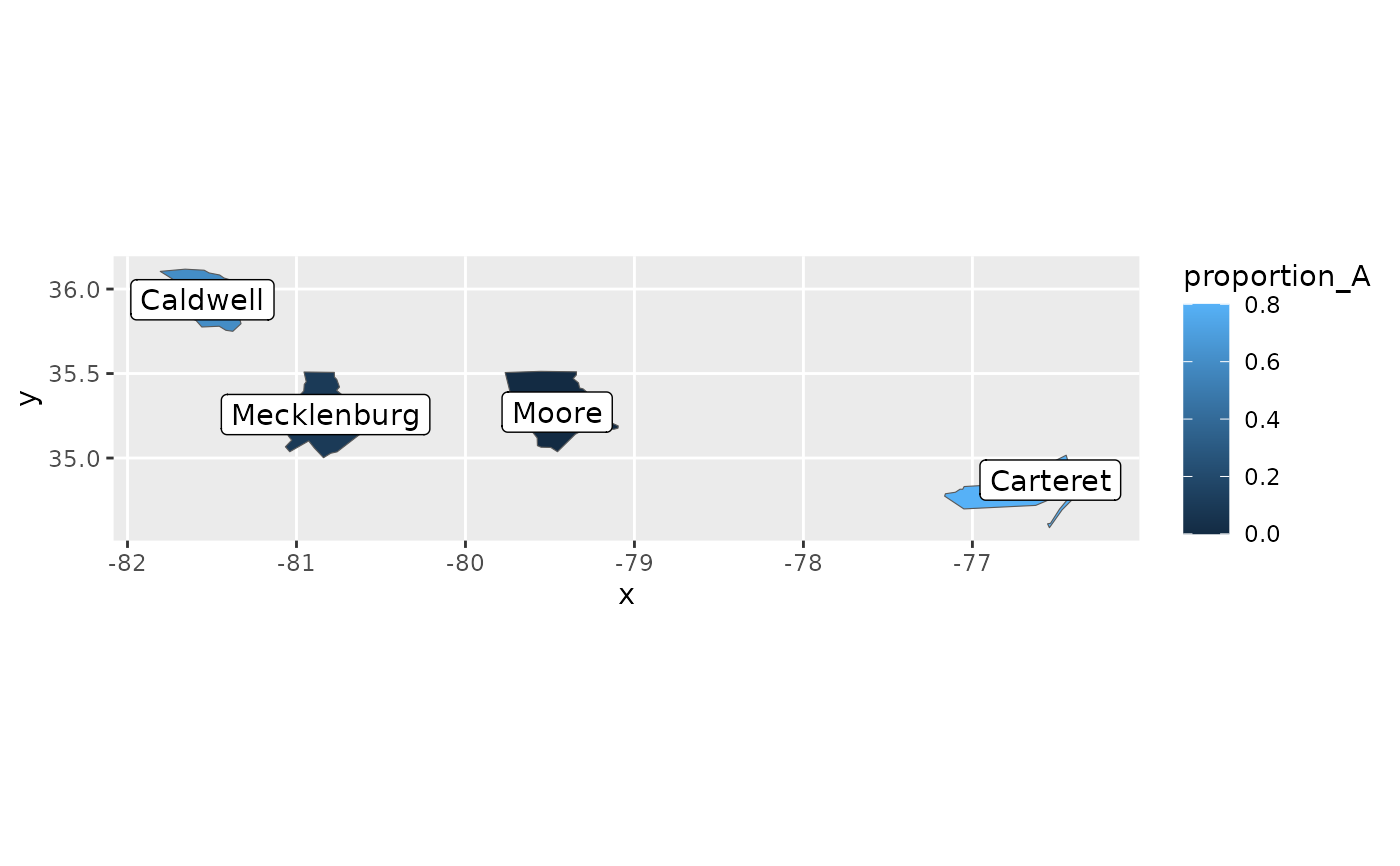
library(ggplot2)
events <- data.frame(
county = c("Mecklenburg", "Carteret", "Moore", "Caldwell"),
proportion_A = c(0.1, 0.8, 0.0, 0.6)
)
ggplot(events, aes(location = county)) +
geom_sf(aes(fill = proportion_A), stat = "automap") +
geom_label(aes(label = county), stat = "automap_coords") +
coord_automap(feature_type = "sf.nc")